Introduction: Early Apartheid: 1948-1970
At a Glance
Language
English — USSubject
- History
- Social Studies
- Democracy & Civic Engagement
Table of contents:
- Triumph of the National Party
- Science, God and Race
- Many Nations
- The Passbook System
- The Defiance Campaign
- The Freedom Charter
- Women Protest
- The Sharpeville Massacre
- The Rivonia Trial
- Shut Down at Home, Organizing Overseas
The roots of apartheid can be found in the history of colonialism in South Africa and the complicated relationship among the Europeans that took up residence, but the elaborate system of racial laws was not formalized into a political vision until the late 1940s. That system, called apartheid (“apartness”), remained in place until the early 1990s and set the country apart, eventually making South Africa a pariah state shunned by much of the world.
Triumph of the National Party
Having aggressively promoted an ideology of Afrikaner nationalism for a decade, the National Party won South Africa’s 1948 election by promising to clamp down on non-white groups. Once in office, the National Party promptly began to institute racial laws and regulations it called apartheid (a word that means “apartness” in Afrikaans). Led by Daniel Malan, a former pastor in the Dutch Reformed Church turned politician, the National Party described apartheid in a pamphlet produced for the election as “a concept historically derived from the experience of the established White population of the country, and in harmony with such Christian principles as justice and equity. It is a policy which sets itself the task of preserving and safeguarding the racial identity of the White population of the country; of likewise preserving and safeguarding the identity of the indigenous peoples as separate racial groups.” 1
- 1D. W. Kruger, ed., South African Parties and Policies 1910–1960 (London: Bowes and Bowes, 1960), available at Politicsweb, accessed July 29, 2015.
Apartheid Era Sign

Apartheid Era Sign
The Reservation of Separate Amenities Act (passed in 1953) led to signs such as the one shown above. The Act prohibited people of different races from using the same public amenities.
By 1948, segregation of the races had long been the norm. But as journalist Allister Sparks noted, apartheid, drawing on racist anthropology and racist theology, “substituted enforcement for convention. What happened automatically before was now codified in law and intensified when possible. . . . [Racism] became a matter of doctrine, of ideology, of theologized faith infused with a special fanaticism, a religious zeal.” 1
Religion was an important aspect of Afrikaner identity. Most Afrikaners were members of the Dutch Reformed Church in South Africa, a strict and conservative Calvinist church that promoted the belief that the Afrikaners were a new “chosen people” to whom God had given South Africa. Journalist Terry Bell explained the role of religion in the outlook of those who supported the National Party: “Afrikaners [saw themselves] as players in the unfolding of the Book of Revelations, upholding the light of Christian civilization against an advancing wall of darkness. . . . It was God’s will that the ‘Afrikaner nation’ . . . linked by language and a narrow Calvinism, had been placed on the southern tip of the African continent.” 2 As a result, they saw themselves as a select group whose right to the land was greater than any other group’s.
The new National Party administration offered a stark view of ethnic categories. As laid out in the Population Registration Act of 1950, these categories were as follows: “white” (“a person who in appearance obviously is, or who is generally accepted as a white person, but does not include a person who, although in appearance obviously a white person, is generally accepted as a coloured person”), “native” (“a person who in fact is or is generally accepted as a member of any aboriginal race or tribe of Africa”), and “coloured” (“a person who is not a white person or a native”). 3 “Indian” was soon added as a fourth group. The groups were not only portrayed as distinct and fundamentally different; drawing on principles of Social Darwinism, they were ranked hierarchically in terms of supposed intellectual capacity and other attributes. The white population stood at the pinnacle of the South African racial hierarchy, with the National Party ideology claiming that they should dominate the other groups because of their natural superiority. Their control of the state guaranteed whites superior access to education, healthcare, employment, and housing. “Natives,” or black South Africans, stood at the very bottom of this steep hierarchy—a necessity in the eyes of Afrikaners, who believed not only that their livelihoods depended on depriving black South Africans of land, voting rights, the right to marry freely, and, above all, the right to participate freely in the labor market but also that Africans were not as deserving as whites of these privileges. Indian and “coloured” groups were “ranked” above black South Africans, allowing them some employment and mobility privileges denied to black South Africans yet still making them subservient to the white South African population.
| nationality | Percent of Population |
|---|---|
| Native | 68.3% |
| White | 19.3% |
| Colored | 9.4% |
| Indian | 3% |
Science, God, and Race
The triumph of the National Party pushed to the forefront of South African racism the ideas fostered by church leaders and scholars in Afrikaner institutions. During the 1930s, scientific books and articles, some written by scholars at Stellenbosch University and the University of Pretoria, lent credence to the idea that white populations were of superior intelligence to nonwhite groups. The Dutch Reformed Church, whose congregations had been segregated since 1857, also preached that, following the Tower of Babel, God had ordained that different cultures be distinct and sovereign. The church’s ideas combined with the pseudoscience of race to give rise to a secular theology of Christian nationalism. If groups were to develop as God intended, they needed to live separately.
Because they conceived of blacks and whites as fundamentally different, Afrikaners concluded that contact between the groups fostered conflict. Each group would prosper most if left to develop on its own; to impose segregation was to protect and promote black culture, they argued. The 1947 National Party campaign pamphlet explained:
The party holds that a positive application of apartheid between the white and non-white racial groups and the application of the policy of separation also in the case of the non-White racial groups is the only sound basis on which the identity and the survival of each race can be assured and by means of which each race can be stimulated to develop in accordance with its own character, potentialities and calling. Hence inter marriage between the two groups will be prohibited.
Within their own areas the non-white communities will be afforded full opportunity to develop, implying the establishment of their own institutions and social services, which will enable progressive non-Whites to take an active part in the development of their own peoples. The policy of our country should envisage total apartheid as the ultimate goal of a natural process of separate development. 4
The reading Apartheid Policies offers a more extended explanation of the ideas behind apartheid, as publicly articulated by the party.
A contradiction arose, however, because if black South African labor had been subtracted from the white South African economy, the latter would have immediately collapsed. While the theory of apartheid argued that the races should be kept separate, the economy of the South African state depended heavily on black South African labor. Therefore, the apartheid state had to permit black South African laborers to come and go between white and black territories.
Many Nations
After the National Party took power, it implemented a series of laws designed both to separate each of the country’s racial groups and to divide and weaken the black South African population and allow for the easy exploitation of its labor. The Population Registration Act created a national system of racial classification that gave every citizen a single identification number and racial label that determined exactly what privileges this person would be able to enjoy. Where one could live, whether one had to carry a passbook to travel, and what sort of education one could receive depended on one’s racial classification. While white South Africans enjoyed every conceivable right, black South Africans could not vote for South African officials, and coloured South Africans could only vote for white representatives—they could not run for office themselves. The Prohibition of Mixed Marriages Act of 1949 banned interracial marriage, while the Immorality Act of 1950 “prohibited sex between whites and non-whites.”
| Law | Year | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Prohibition of Mixed Marriages | 1949 | Banned marriage between whites and non-whites. |
| Population Registration Act | 1950 | Created a national register in which every individual’s race was officially recorded. |
| Group Areas Act | 1950 | Legally codified segregation by creating distinct residential areas for each race. |
| Immorality Act | 1950 | Prohibited sex between whites and non-whites. |
| Suppression of Communism Act | 1950 | Outlawed communism. Allowed detention on communism charges of those who objected to or protested apartheid. |
| Bantu Authorities Act | 1951 | Created black homelands and governments. |
| Separate Representation of Voters Act | 1951 | Removed coloureds from voter rolls. |
| Bantu Education Act | 1953 | Set up a separate educational system for black South Africans, charged with creating an “appropriate” curriculum. |
| Native Resettlement Act | 1954 | Allowed the removal of black South Africans from areas reserved for whites. |
| Extension of Education Act | 1956 | Excluded black South Africans from white universities. Set up separate universities for each racial group. |
| Terrorism Act | 1967 | Allowed indefinite detention without trial of opponents of apartheid and created a security force. |
The Group Areas Act of 1950 was the Malan government’s first attempt to increase the separation between white and black urban residential areas. The law was both a continuation of earlier laws of segregation and a realization of an apartheid ideal that cultures should be allowed to develop separately. The law declared many historically black urban areas officially white. The Native Resettlement Act of 1954 authorized the government to force out longtime residents and knock down buildings to make room for white-owned homes and businesses. Whole neighborhoods were destroyed under the authority of this act. For example, on February 9, 1955, Prime Minister Malan sent in 2,000 police officers to remove the 60,000 residents of Sophiatown, a vibrant African neighborhood in central Johannesburg. Black South African residents were forcibly resettled in the Meadowlands neighborhood of Soweto, where they were expected to move into houses without electricity, water, or toilets. In Durban, Indian neighborhoods faced a similar fate. City centers became enclaves for the white South African population, while black, coloured, and Indian South Africans were relegated to townships at the periphery of the urban areas, which were often far removed from centers of employment and resources such as hospitals and recreation spaces. Generally, the townships were intended to contain the black South African population by restricting movement through urban planning while ensuring that black South Africans had permission to leave these areas in order to work.
- 1Allister Sparks, The Mind of South Africa: The Story of the Rise and Fall of Apartheid (Johannesburg: Jonathan Ball Publishers, 2006), 190.
- 2Terry Bell, Unfinished Business: South Africa, Apartheid and Truth (London: Verso, 2003), 23.
- 3Population Registration Act (1950), Wikisource entry, accessed July 27, 2015.
- 4D. W. Kruger, ed., South African Parties and Policies 1910–1960 (London: Bowes and Bowes, 1960), available at Politicsweb, accessed July 29, 2015.
Bantustans in South Africa
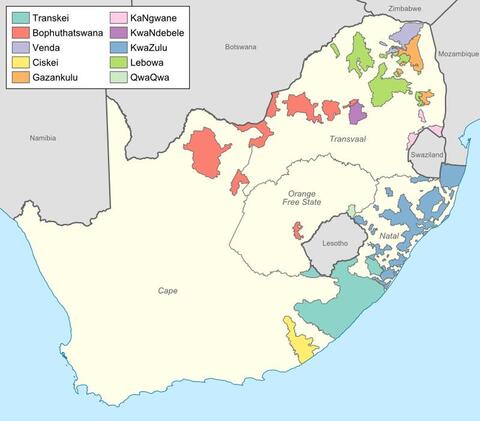
Bantustans in South Africa
With the passing of the Bantu Authorities Act in 1951, the apartheid set in motion the creation of ten bantustans in South Africa, illustrated in this map.
Apartheid laws treated black South Africans not as citizens of South Africa but rather as members of assigned ethnic communities. The Bantu Authorities Act (1951) and the Bantu Self-Government Act (1959) created ten “homelands” for black South Africans, known as Bantustans, and established new authorities in the Bantustans. While the apartheid state portrayed the Bantustans as a system that offered black South Africans independence, giving the appearance of self-government, the leaders of the homelands were appointed by the apartheid state. Furthermore, black South Africans were assigned these ethnic identities and corresponding “homelands” even if they did not see this as a central aspect of their identity. Black South Africans were essentially stripped of their South African citizenship.
By making black South Africans citizens of Bantustans, the government deflected any possible criticisms of refusing them the right to vote in South Africa. But this arrangement also very deliberately created a system of migrant labor. Since the homeland areas, which were mostly rural and underdeveloped, offered inhabitants few employment opportunities, most had to search for work in cities and live temporarily in townships. Given the desperate situation in the homelands, the apartheid state was ensured of a regular source of cheap labor for white-owned businesses and homes.
Although they were said by apartheid authorities to bear a historical association with the different kingdoms, Bantustans were scattered around the fringes of the country without any consideration for the well-being of their residents. KwaZulu in Natal, for example, was divided into many pieces, separated by large areas designated as white. The apartheid government reserved urban areas, the most desirable farmland, and regions rich in natural resources for white South Africans, while it allocated the least arable land for the Bantustans. Although black South Africans constituted nearly 70% of the population, only 13% of South Africa’s territory was allocated to the Bantustans. The reading A Wife’s Lament offers a look at how the creation of the homelands affected black South African families.
Girl Walking to School, Mthatha

Girl Walking to School, Mthatha
A child walks to school through the barren village of Qunu, South Africa, located just outside of the town of Mthatha.
Dividing the black South African population into Bantustans was in part intended to break the solidarity that had formed between groups of black South Africans in the face of white oppression. By cultivating a false sense of “tribal” belonging, the government sought to reduce the black South African population to many small, ineffective groups, channeling discontent from resistance to apartheid into internal bickering.
A decade after the rise of the National Party, many black South Africans found themselves effectively stateless. They could only enter white areas to work, and they needed documents authorizing them to do so.
The Passbook System
By the middle of the twentieth century, vast numbers of black South Africans commuted daily from Bantustans and townships to the white areas where they worked. Various forms of internal passports had existed in South Africa since the early twentieth century, but the apartheid government expanded and formalized the pass system. Designed to satisfy both the need for black labor and the need to protect white advantages, “pass” laws required every black male over the age of 16 to carry a passbook, which contained a photograph, fingerprints, a racial classification, place of work, and the bearer’s police record.
Additionally, the passbook had to have a current signature from an employer and proof that the bearer had paid income taxes. The passbook bureaucracy was so convoluted that few people were able keep their records current, providing authorities with an excuse for detaining black South African men at will. Anyone living in a black township on the outskirts of a white city who did not possess appropriate papers was effectively treated as an illegal alien and subject to arrest. Those found in violation were sometimes imprisoned, often forced to pay fines, and sometimes sent back to their homelands. Eventually, black South African women were also required to carry passes, an act that had a tragic impact on the lives of tens of thousands of families who were not allowed to live together. Only a few of these women with formal salaried employment were able to secure the necessary passes and keep them current, thereby satisfying the authorities’ requirements to be legally living in the same house as their husbands. Most black South African women were forced to remain in the homelands, raising their children and eking out a living off the land while their husbands worked in the cities or on white-owned farms.
Most black South Africans were obliged to leave “white areas” by sunset. At the country’s many checkpoints and roadblocks, black South Africans were at the mercy of the police and could summarily be stopped, arrested, and deported to homelands. Thousands of black South Africans were forced to break the law on a daily basis as they searched for work or attempted to keep their families together.
Police carried out daily raids on black residences, bursting in at midnight, forcing residents to show their passes, and arresting those out who did not have them. Police brutality was rife; hundreds of thousands of black South Africans were arrested, thousands disappeared from their homes without a trace, and hundreds lost their lives to the guns and batons of law enforcement officials. The government recruited black South Africans to join the police force and serve as informants, torturers, and, in some cases, executioners, and for a variety of reasons (bribes, economic pressures, and scare tactics), some black South Africans helped the government enforce apartheid. The reading Experiencing Apartheid gives an account of how the draconian enforcement of apartheid laws could affect black South Africans.
The Defiance Campaign
As apartheid laws were implemented, South Africa’s black leaders looked for a way to protest the changes imposed by the minority white government. Denied the right to vote, they had to find other means of expressing opposition outside the formal political system. From 1950 to 1952, the African National Congress (ANC) organized mass actions, which included boycotts, civil disobedience, demonstrations, and strikes.
The Defiance Campaign

The Defiance Campaign
A group of resisters proudly pose after their release from prison in Durban during the Defiance Campaign Against Unjust Laws, 1952.
Launched in April 1952, on the 300th anniversary of the arrival of the first Dutch colonists, this Defiance Campaign became the largest campaign of civil disobedience in South Africa’s history up to that point. It was also the first multiracial mass-resistance campaign, and its unified leadership included representatives from the African National Congress, the South African Indian Congress, and the Coloured People’s Congress. Together with other groups, these organizations formed the Congress Alliance, which forged a multiracial front against the implementation of apartheid. 1 Following heavily attended demonstrations in a number of towns, defiance of the newly erected racial laws commenced on June 26, 1953. Ten thousand volunteers, organized by the leader of the ANC Youth League, 34-year-old Nelson Rolihlahla Mandela, were instructed to enter forbidden areas without passes, use entrances designated “Europeans only,” and occupy “white only” counters and waiting rooms. 2 These violations were designed to flood the prison system, rendering law enforcement impossible.
- 1For Nelson Mandela’s description of the first months of the campaign and the unity between the different groups, see “We Defy—10,000 Volunteers Protest Against Unjust Laws,” August 30, 1952, African National Congress website, accessed July 27, 2015.
- 2Reader’s Digest Illustrated History of South Africa: The Real Story, 3rd ed. (Cape Town: The Reader’s Digest Association Limited, 1994), 385.
Nelson Mandela, 1937

Nelson Mandela, 1937
A young Nelson Mandela poses for a photograph in Umtata shortly before moving to Fort Beaufort to attend Healdtown Comprehensive School.
A decade later, Mandela reflected on the goals and strategies behind the Defiance Campaign:
Even after 1949, the ANC remained determined to avoid violence. At this time, however, there was a change from the strictly constitutional means of protest which had been employed in the past. The change was embodied in a decision which was taken to protest against apartheid legislation by peaceful, but unlawful, demonstrations against certain laws. Pursuant to this policy the ANC launched the Defiance Campaign, in which I was placed in charge of volunteers. This campaign was based on the principles of passive resistance. More than 8,500 people defied apartheid laws and went to jail. Yet there was not a single instance of violence in the course of this campaign on the part of any defier. I and nineteen colleagues were convicted for the role which we played in organising the campaign, but our sentences were suspended mainly because the judge found that discipline and non-violence had been stressed throughout. 1
The government lashed out, arresting over 8,000 South Africans and handing out stiff penalties and long prison sentences to those who had broken apartheid laws. It adopted the Public Safety Act (1953), which allowed the president to suspend all existing laws, stripping away basic civil liberties. “The government saw the campaign,” Mandela later recalled, “as a threat to its security and its policy of apartheid. They regarded civil disobedience not as a form of protest but as a crime, and were perturbed by the growing partnership between Africans and Indians. Apartheid was designed to divide racial groups, and we showed that different groups could work together. The prospect of a united front between Africans and Indians, between moderates and radicals, greatly worried them.” 2
While the Defiance Campaign lost momentum after a few months, and it did not achieve many concessions from the government, it was a turning point for South Africa. For the liberation movement, it was the first mass campaign, swelling the membership ranks of the ANC from just 7,000 to 100,000 and helping to transform the group from an elite organization into a mass movement. 3
The Freedom Charter
In early 1955, the ANC organized a listening campaign, in which they sent out 50,000 volunteers to talk with people across the country about their political hopes for South Africa. In June 1955, the ANC, along with several other anti-apartheid political organizations—the South African Indian Congress, the Coloured People’s Congress, the South African Congress of Trade Unions, and the Congress of Democrats—developed a set of political demands that drew on the results of these interviews. The “Freedom Charter,” as it became known, called for a nonracial South Africa, in which people of all races would have equal rights and would share in the country’s wealth.
The Freedom Charter became the political agenda for the ANC, shaping its actions over the next several decades. The charter called for rights for all South Africans, not just black South Africans, and this concept of nonracialism became an important principle behind the ANC’s approach to political change. The Freedom Charter served as the guiding document for the ANC in its struggle against apartheid and beyond, as its nonracialism ultimately became a basis for ANC policies after the fall of apartheid. The reading The Freedom Charter includes the text of this foundational document.
Women Protest
Although their role has often been overlooked in historical accounts of resistance to apartheid, black South African women played an important part in opposing the system of racial segregation. (White and “coloured” women were part of the resistance, but the vast majority were black South Africans.) In the early 1900s, black South African women successfully resisted proposed legislation that would require them to carry passbooks. After a setback in 1918, women organized again to end the practice altogether under the leadership of Charlotte Maxeke, a gifted singer, social worker, and activist—a hero of the early days of protest. She was called “the mother of African freedom in this country” by A. B. Xuma, who served as the president of the ANC in the 1940s. 4
- 1Nelson Mandela, “An Ideal for Which I Am Prepared to Die,” The Guardian, April 22, 2007, accessed July 27, 2015.
- 2Nelson Mandela, Long Walk to Freedom: The Autobiography of Nelson Mandela (Boston: Little, Brown and Company, 1994), 116.
- 3For a full and vivid description of the campaign, see Monty Naicker, “The Defiance Campaign Recalled,” June 30, 1972, African National Congress website, accessed July 27, 2015.
- 4Andile Mnyandu, “Charlotte Maxeke,” eThekwini Municipality website, accessed July 27, 2015.
Woman Showing Her Passbook
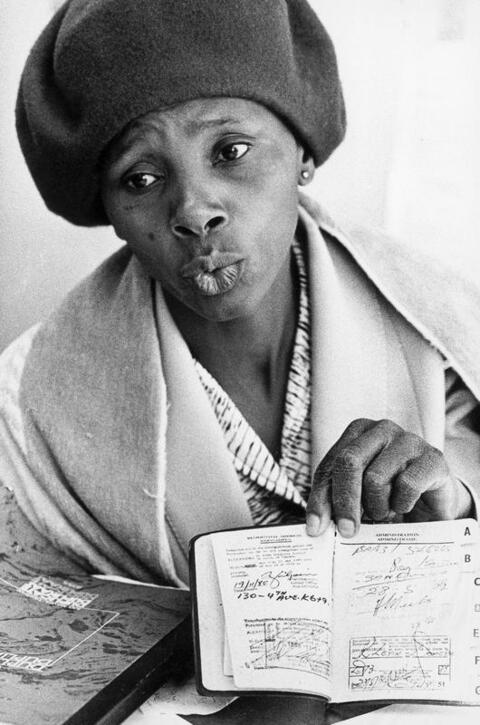

Woman Showing Her Passbook
An unidentified black South African woman defiantly shows her passbook.
The multiracial Federation of South African Women was formed in the 1950s, representing hundreds of thousands of women. Together with the ANC Women’s League, the federation organized many local demonstrations against the pass laws, culminating in the March on Pretoria. On August 9, 1956, about 20,000 women peacefully gathered in front of the city’s Union Buildings. They stood in silence for 30 minutes and then, breaking the quiet, chanted a call to the prime minister: “Wathint’ abafazi, wathint’ imbokodo!” (Now that you have touched the women, you have struck a rock!) Alerted to the protest ahead of time, the prime minister, J. G. Strijdom, had slipped out of town. Before they concluded their protest, activists left on the prime minister’s door a petition bearing the signatures of 100,000 women. Their chant became the slogan for future women’s protests. The reading Women Rise Up against Apartheid and Change the Movement features a firsthand account of the 1956 women’s march.
The Sharpeville Massacre
By the late 1950s, a growing number of activists questioned the tactics of the African National Congress. The young founders of the Pan Africanist Congress (PAC), formed in 1959, believed that only an all-black African organization, in league with anti-colonial Africans throughout the continent, could adopt the forceful posture necessary to overcome apartheid. The time had come, these firebrands believed, to reclaim the land stolen by whites. In his inaugural speech, Robert Mangaliso Sobukwe, head of the PAC, outlined their approach:
[W]e reject both apartheid and so-called multi-racialism as solutions of our socio-economic problems. . . . To us the term “multi-racialism” implies that there are such basic insuperable differences between the various national groups here that the best course is to keep them permanently distinctive in a kind of democratic apartheid. That to us is racialism multiplied, which probably is what the term connotes. We aim, politically, at government of the Africans by the Africans, for the Africans, everybody who owes his only loyalty to Afrika and who is prepared to accept the democratic rule of an African majority being regarded as an African. 1
Questioning the effectiveness of nonviolence against apartheid, the PAC set up a military wing, Poqo, that was feared by the white establishment.
The PAC announced to authorities that it would lead a peaceful demonstration against pass laws in the township of Sharpeville on March 21, 1960. Some 5,000 protesters gathered in the town center and then marched toward the police station to turn themselves in for defying pass laws. 2 Around midday, the police panicked and opened fire on the demonstrators, killing 69 people and wounding another 180. Most were shot in the back as they fled.
Black South African leaders called for a day of mourning and a “stay-at-home” strike on March 28, 1960. Hundreds of thousands of black South Africans did not show up for work that day, making it the first successful national strike in the nation’s history. Marches took place in Johannesburg, Durban, and Cape Town; the largest included a group of 30,000 who marched from Langa to Cape Town, led by 23-year-old Philip Kgosana. Fearing that black protests might spread, the government acted decisively in the aftermath of the Sharpeville massacre. It declared a state of emergency and arrested more than 11,000 people, including the leaders of both the ANC and the PAC. On April 8, the government banned both organizations. This put an abrupt end to the protests and ushered in a period of harsh repression that lasted for more than a decade.
During the 1960s, the government intensified its policies against the anti-apartheid movement by severely restricting the ability of the movement’s leaders to speak in public and to mobilize the population. The government went on to scrap what few rights non-white workers had, including the rights to organize, bargain, and strike, and it also intensified efforts to shut down surviving black urban neighborhoods and move the black population to the townships and homelands.
Although officially banned, the ANC continued to function clandestinely. The young leadership of the ANC, having seen their hopes for change dashed so violently, began to discuss a new approach to resistance. Despite opposition from the old guard, in 1961 the young upstarts prevailed: while there would never be official ANC approval, the creation of an armed wing was tacitly accepted. Named Umkhonto we Sizwe (“Spear of the Nation,” known as MK), the clandestine group had Nelson Mandela as its commander.
Such a group needed new skills and new partners. Mandela and the other militant ANC members formed an alliance with the South African Communist Party, a multiracial political organization with ties to the Soviet Union that had been banned in 1950 but remained active underground, working primarily to support the interests of workers. They based MK operations at a farm in Rivonia, not far from Johannesburg. Setting up a network of operatives committed to terror permitted MK, over a year and a half, to carry out approximately 200 attacks on government facilities. By January 1962, Mandela had traveled to Algeria, where he learned the basics of guerrilla warfare from members of that nation’s National Liberation Front. A fortnight after his return to South Africa, he was arrested on the charges of inciting workers to strike and leaving the country without a passport. A year later, Mandela’s MK comrades were arrested at their Rivonia training camp.
The Rivonia Trial
In 1963, three years after the terror of the Sharpeville massacre carried out by government forces, the Rivonia Trial began with the government seeking to accuse its opponents of fomenting violence. Ten defendants, including six black Africans, three white Jews, and the son of an Indian immigrant, were charged with sabotage and attempting to violently overthrow the government of South Africa.
During the trial, the defendants decided not to deny the charge of sabotage. They wanted the world to know what they had done and why. Their lawyers expressed misgivings about their decision, because it meant that they could be put to death for treason. But the revolutionaries felt that they had to take the risk, using the trial to make their positions known to every person in South Africa.
When he took the stand at the Pretoria Supreme Court, Mandela described his personal journey within the resistance movement, explaining the reasoning behind the adoption of a militant approach. (The reading Mandela on Trial includes the text of this testimony.) The prosecutor attempted to prove that the group, which he labeled communist, was plotting to overthrow the government of South Africa. He played on Afrikaner fears of Soviet revolutionary plots. The government had long presented itself as a true ally of the West, securing generous financial and military support—a position unusual among African states, many of which adopted socialism as a reaction against the colonial powers they had thrown off.
When the trial ended in June 1964, two men had been acquitted. Six of the remaining eight, including Mandela, were found guilty on all counts and sentenced to life in prison.
Shut Down at Home, Organizing Overseas
In the aftermath of the Sharpeville massacre and the government crackdown that followed, the ANC leadership charged Oliver Tambo, the organization's deputy president, with the task of beginning to organize overseas. With protest nearly impossible within the country and so many top ANC leaders in prison, Tambo looked for new ways to fight against the apartheid regime. Making use of a home base in London, he lobbied international leaders to speak out against the brutality in his homeland. Almost immediately, Tambo and British anti-apartheid movement activists organized to have South Africa removed from the British Commonwealth, an intergovernmental organization made up of countries that were formerly part of the British Empire—a move that succeeded in 1961. At the same time, activists began to lobby against South Africa in the United Nations, winning a 1962 vote at the UN General Assembly for a trade ban on South Africa. A partial arms ban followed a year later. Further international pressure against South Africa’s discriminatory policies came from the International Olympic Committee, which first suspended South Africa from participating in the 1964 Tokyo Olympics and then formally banned the country from the Olympics in 1970. The ANC, with Tambo’s leadership, eventually set up 27 overseas missions.
However, diplomacy was only one part of the strategy. In 1965, the countries of Tanzania and Zambia agreed to let the ANC’s unofficial armed wing, Umkhonto we Sizwe (MK), set up paramilitary training camps. Under the leadership of Abongz Mbede and Joe Slovo, a South African Jew whose family emigrated from Lithuania, the MK sought to bring what they called an “armed struggle” to South Africa. In the late 1960s, though, South Africa was surrounded by neighbors that were allies of the apartheid government, making it difficult for fighters to make it into the country. An official history of the ANC describes the situation:
The ANC consultative conference at Morogoro, Tanzania in 1969 looked for solutions to this problem. . . .The Morogoro Conference called for an all-round struggle. Both armed struggle and mass political struggle had to be used to defeat the enemy. But the armed struggle and the revival of mass struggle depended on building ANC underground structures within the country. A fourth aspect of the all-round struggle was the campaign for international support and assistance from the rest of the world. These four aspects were often called the four pillars of struggle. The non-racial character of the ANC was further consolidated by the opening up of the ANC membership to non-Africans. 3
- 1“Robert Sobukwe Inaugural Speech, April 1959,” African National Congress website, accessed June 2018.
- 2David James Smith, Young Mandela: The Revolutionary Years (New York: Little, Brown and Company, 2010), 210.
- 3“A Brief History of the African National Congress,” African National Congress website, accessed June 2018.
How to Cite This Reading
Facing History & Ourselves, “Introduction: Early Apartheid: 1948-1970,” last updated August 3, 2018.
This reading contains text not authored by Facing History & Ourselves. See footnotes for source information.












